WHAT IS E-WASTE
Electronic waste or e waste, is an umbrella term, encompassing all electronic appliances, products, components, and accessories that are broken, discarded, obsolete or have reached the end of their product life cycle. Because of its sheer nature and hazarduous constituting elements, such as chemical substances, plastic, metals, etc., it is imperative to ensure that e waste is properly managed and treated.
The e waste Management Rules (2016) state that every producer/manufacturer generating e waste, in addition to the consumers using them, is liable by law to recycle the scrap through an authorized channel.

CLASSIFICATION OF E-WASTE
e waste can be classified on the basis of its composition and component, or on the basis of the utility and purpose served. Ferrous and nonferrous metals, glass, plastics, pollutants, and other are the six categories of materials reported for e waste composition. Given below is a check-list of the various kinds of commonly found electronic appliances available easily at your home/office, which, upon reaching the end of its product life cycle, becomes e waste. Do you have any of these products simply lying around? Call us on our toll-free number and raise a pickup request today!


THE DIGITAL DARK AGE
- In 2019, 282.9 million phones were sold in India
- On an average an individual replaces his phone every 2 years.
- 300 million computer and 1 billion cellphones go into production every year.
- It takes 245 kgs of fossil fuels, 20 kgs of chemicals and 1.5 tons of water to manufacture one computer and monitor.
WHY RECYCLE E-WASTE?
A wise man once said, “We do not inherit the Earth from our ancestors, rather, we borrow it from our future children.” And thus, it is our responsibility to re-use, reduce and recycle e waste to ensure that we hand it over to the coming generation in a condition better than how we had received it. Furthermore, allowing the e waste to simply lie around or be mismanaged is hazarduous for life. Many electronic devices contain toxic chemical substances. When they are not handled properly, this e waste is tossed into landfills, and the chemicals present in it leach into the soil, polluting the ground water as well as the air. Recycling electronic and electrical scrap is also an efficient cost-saving, energy-preserving technique. Electronics are made of components that contain valuable raw materials, such as copper and aluminium, or even platinum and gold. Thus, recycling old devices not only saves energy, but also lowers the cost, for fewer raw materials are required to manufacture new equipment. Hulladek is a licensed PRO, which means that it is entitled to provide CSR certificates to companies recycling their e waste conscientiously. Thus, corporates too, can build their goodwill by managing their e waste with us.

HUMAN HEALTH HAZARDS
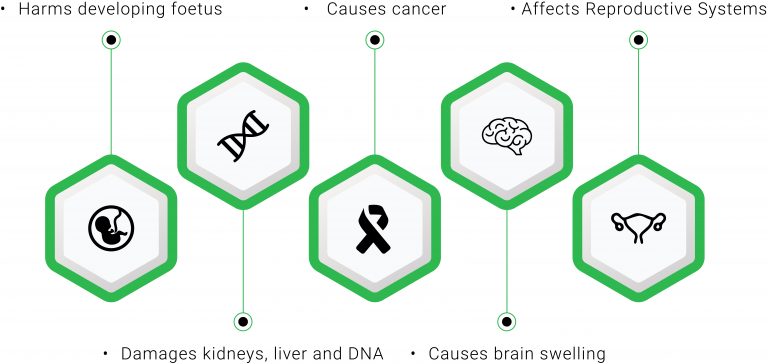
Did you know? About 95% of India’s e waste is treated and processed in urban slums, where untrained workers carry out unsafe e waste disposal practices that are catastrophic for both – human and environmental health. This is owing to the fact that electronic waste is made up of plastic and toxic chemicals, and contains pollutants such as dioxins from lead, beryllium, cadmium, mercury, etc. Thus, when e waste is managed in efficiently, these substances enter the environment, and get mixed into the air we breathe and water we consume – which, in turn, poses the risk of these toxins entering the human body.
WHAT IS CO2 FOOTPRINT?
A carbon footprint is the total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions caused by an individual, event, organization, service, place or product, expressed as carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e). Greenhouse gases, including the carbon-containing gases carbon dioxide and methane, can be emitted through the burning of fossil fuels, land clearance, and the production and consumption of food, manufactured goods, materials, wood, roads, buildings, transportation and other services.

